Lithium forklift Batteries: Complete Guide [Advantages, disadvantages, costs]
Curious about lithium forklift batteries?
Then you've come to the right place.
Because in this article, we'll cover everything you need to know about them!
These include:
The main difference between lithium-ion batteries and lead-acid batteries
The main features, advantages and benefits of lithium-ion batteries
What should I pay attention to before considering switching to lithium-ion batteries
Leading manufacturer of lithium-ion forklift batteries
Lithium-ion forklift battery how much
And so much more...
Let's get started!
Is it worth buying lithium forklift batteries?
The short answer is: If you are a medium to large business that runs multiple shifts, then lithium-ion forklift batteries may be a very good choice for you.
Why?
Because although the current price of lithium forklift batteries is higher compared to lead-acid batteries, they can save a lot of costs in the long run.
The return on investment of lithium forklift batteries is also typically achieved within 36 months.
Overall, lithium-ion forklift batteries are 40% more energy efficient than lead-acid batteries. 88% more energy efficient than diesel batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries are designed to last longer, making them ideal for operations where battery replacement is inconvenient.
They can also withstand extremely low temperatures without failure, making them ideal for outdoor applications.
Lithium-ion and lead-acid forklift batteries
There are two basic power supply types for electric forklifts (forklift batteries) : lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries.
But what exactly is the difference between the two technologies?
Lead-acid battery chemistry
Lead-acid batteries have long been the most common type of battery. Its technology dates back to the mid-19th century. Lead-acid batteries for forklifts are also known as "wet batteries" and are relatively cheap.
Lead-acid batteries generate electricity through an electrochemical reaction between a lead plate and a 30 to 50 percent mixture of sulfuric acid and distilled water, called an "electrolyte solution."
The components of a lead-acid battery include:
cell
saloon
Lead dioxide sheet
cable
electrolyte
To generate electricity, an electrochemical reaction takes place between the lead plate and the electrolyte solution.
Electric ions flow from sulfuric acid to the negative plate, producing electricity.
Lead-acid battery charging

Lead-acid batteries take longer to charge than lithium-ion batteries. Charging is usually done the traditional way, usually after a shift, using a low current to charge for about 8 to 10 hours until fully charged. After a longer charging time, it takes 6 to 8 hours to cool down before you can use the battery again.
Traditional charging is mostly carried out at night and is most suitable for single shift operation.
This also means that lead-acid batteries are not usually recharged by chance. This quickly damages the battery, making it wear out faster and shortening its cycle time.
Overall, lead-acid forklift batteries have a short lifespan: typically three to five years (or 1,000 to 1,500 charge cycles) at normal 40-hour weekly operation.
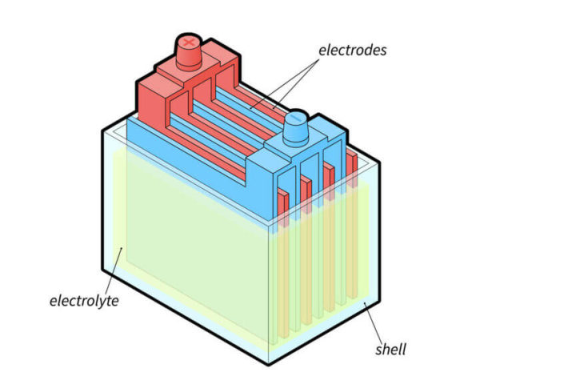
Lithium-ion battery chemistry
Over the past few decades, lithium-ion batteries have become more widely used in consumer electronics. Now, lithium-ion is becoming an increasingly popular technology for powering forklifts.
The lithium-ion forklift battery consists of the following parts:
The cathode,
Electrolyte (lithium),
Anode,
Delimiter, as well
2 current collectors (positive and negative).
In order to generate electricity, different chemical reactions occur in lithium-ion batteries, of which the most popular for forklifts is lithium iron phosphate.
The anode and cathode store lithium. When a lithium-ion battery discharges, the electrolyte moves from the anode to the cathode through a diaphragm, transporting positively charged lithium ions from the anode to the cathode.
When the battery is charged, the electrolyte liquid moves from the cathode to the anode through the diaphragm, carrying negatively charged lithium ions.
Lithium-ion batteries are easy to charge with opportunistic charging because they are fast charging. This charging method uses a dedicated charger with a high current to quickly charge the battery.
It can be charged on demand or at the most convenient time, thereby increasing the efficiency of lithium-ion batteries.
When properly maintained, lithium-ion forklift batteries have a service life of 2,000 to 3,000 cycles, or 300 working days per year, and a service life of about 7 to 10 years.
Advantages of lithium-ion forklift battery
Lithium-ion batteries can improve the efficiency of your operations.
If the investment conditions are right, charging space is available, and the budget allows, there are several key factors that may motivate you to adopt this energy solution.
Increase productivity

Lithium-ion forklift batteries take less time to charge than lead-acid batteries, which also require rest periods before they can be used again.
Lithium-ion batteries can be fully charged in less than 2 hours and do not require the same cooling period as lead-acid batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries can be charged in 15-30 minutes, which is called opportunistic charging, and you can charge them during lunch, rest, or when the forklift is idle for a few minutes. This allows for multiple shifts.
In addition, lithium-ion batteries last longer after a single charge than lead-acid batteries.
Compared with the linear discharge curve of the lead-acid battery, the discharge curve of the forklift lithium battery is much flatter. This means that over a wide operating range, the voltage change of the battery terminals is very small, and the battery can hold more power even when it is almost fully discharged.
You can use more than 80% of the state of charge (SoC), but you can't use zero. When SoC reaches zero, there may still be power left in the battery, and continued discharge may damage the battery.
With lithium-ion batteries, your fleet will benefit from shorter downtime as well as higher productivity and output.
Opportunistic charging

Forklift battery charging is an important factor to consider.
You can charge the lithium-ion forklift battery during a 15-30 minute break during the day (called opportunity charging). Although you can charge a lead-acid battery, this will shorten the battery life.
In addition, lithium-ion batteries can be fully charged in as little as 1 hour and up to 2 hours. This is eight times faster than lead-acid batteries and requires no cooling time.
That's how one lithium-ion battery can power three shifts. Their energy storage capacity has increased by four times and their energy efficiency has increased by 30%.
Reduce maintenance
As with forklift maintenance, forklift batteries also need maintenance.
If lead-acid batteries are not properly maintained, they can undergo a chemical process called battery sulphation. This can cause damage to the battery. Therefore, you must maintain the water and electrolyte levels in the battery, regularly replenishing the battery with distilled water to keep it healthy. Maintenance can be time-consuming and expensive.
This is unlike lithium-ion batteries, which require little maintenance.
Lithium-ion batteries do not require the addition of water or frequent maintenance procedures such as balanced charging and cleaning.
They come with sealed batteries that you can keep running without cleaning or adding water. This also reduces maintenance effort and costs.
In addition, depending on your operation, you don't have to remove or replace the battery within the working day, as the lithium-ion battery can be retained in the forklift for longer.
No need to water, remove batteries, or perform other maintenance also means no watering areas or maintenance areas, saving facilities and storage space.
Energy conservation
Lead-acid batteries consume power when discharged, charged, or idle, leaving only about 80% of the energy used to charge the battery available for output. This makes lead-acid batteries energy inefficient and increases the cost of electricity.
Lithium-ion batteries, on the other hand, are more energy efficient because they have minimal losses and most of the energy used for charging can be used as output, sometimes up to 99%.
Therefore, lithium-ion batteries can help you reduce your electricity costs because they provide more output due to minimal energy loss.
Support multi-shift operation
If your daily operation lasts 16 or 24 hours, the battery charge time is crucial for smooth operation.
Why?
Typical battery discharge time is about 6 to 8 hours.
This is the key difference between lead-acid forklift batteries and lithium-ion forklift batteries.
A typical lead-acid battery requires about 8 hours of charging time followed by 8 hours of cooling time. This takes about 16 hours before the battery can be used again.
Therefore, for multi-shift operations, you may need 2 to 3 lead-acid batteries per forklift, otherwise you will experience downtime.
Lithium-ion forklift batteries can be fully charged in 2 hours or less, with no cooling time required. In addition, you can charge a lithium-ion battery in 15-30 minutes, which is called opportunistic charging.
This allows charging during breaks or when the forklift is idle, and only one battery per forklift can support multiple shifts.
safer
Forklift battery safety is an important factor in forklift operation. OSHA data shows that most battery-related accidents occur during battery movement or watering.
Because lead-acid batteries are composed of two high-risk chemicals (sulfuric acid and lead), they pose a safety hazard to operators and the environment. Sulfuric acid can touch and burn the skin or eyes of workers who need to wear personal protective equipment such as splash-proof goggles, acid-resistant aprons, face masks and rubber gloves.
Lead-acid batteries are also highly explosive, and there is a risk of explosion when charging, especially if the charging room is poorly ventilated. Among other measures, you will need to install hydrogen sensors in lead-acid battery storage and charging rooms.
Lithium-ion forklift batteries are different.
Lithium-ion batteries are much safer than lead-acid batteries because they don't pose as many health risks/hazards.
They are completely sealed, eliminating the need for the operator to open the battery compartment to add water, reducing the risk of electrolyte spills, toxic fumes, or sulfation like lead-acid batteries.
This also means that PPE is not required, which reduces operating costs and warehouse security.
In addition, lithium-ion batteries do not overheat, so they do not heat up. Maybe they're only five or six degrees warmer.
Reduce the need for charging equipment
If you use lead-acid batteries, you may need multiple batteries per forklift during operation. This may also require you to save additional storage space.
In addition, you need to ensure a safe storage environment, away from hot air pipes and other heat sources, away from direct sunlight, and well ventilated. You must also follow a safe charging process to avoid acid spills or leaks that can cause burns, corrosion, and other hazards.
All of these guidelines require trained personnel and resources. But lithium-ion batteries are easy to charge and require little maintenance. You don't need additional storage infrastructure because you don't need multiple batteries per forklift.
Higher return on investment
Lithium-ion forklift batteries last longer than lead-acid batteries.
With good maintenance, the life of the lead-acid battery can reach 1,500 times, while the life of the lithium forklift battery can reach 3,000 to 4,000 times.
Intermittent charging for a few minutes (e.g., 3 to 15 minutes) shortens the life of lead-acid batteries, but not lithium-ion batteries.
And, if you run lithium-ion batteries on a forklift for about 3,000 + hours per year, you can realize a return on your investment in less than 36 months.
What say you?
You don't need to buy extra batteries (for replacement) because they charge quickly (allowing for chance charging). This also saves facility space.
You don't need more charging stations. Compared to lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion chargers are very small, saving facility space.
Random charging and fast charging do not cause damage. You can charge a lithium-ion battery during a 15-30 minute break (called random charging). While you can charge a lead-acid battery, this can burn out the battery and shorten its life.
Reduce downtime. Random charging helps reduce downtime and improve fleet performance. In addition, lithium-ion forklift batteries last 4 times longer than lead-acid batteries, increasing your efficiency.




