Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) and Li-ion batteries are two different types of battery technologies that differ significantly in their construction, working principles, and applications. Here is a detailed comparison of the two battery technologies:
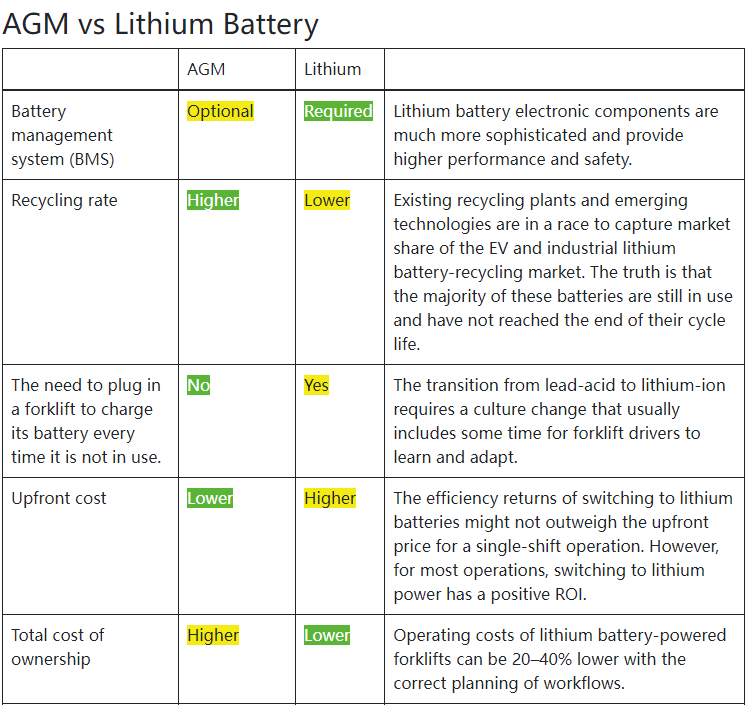
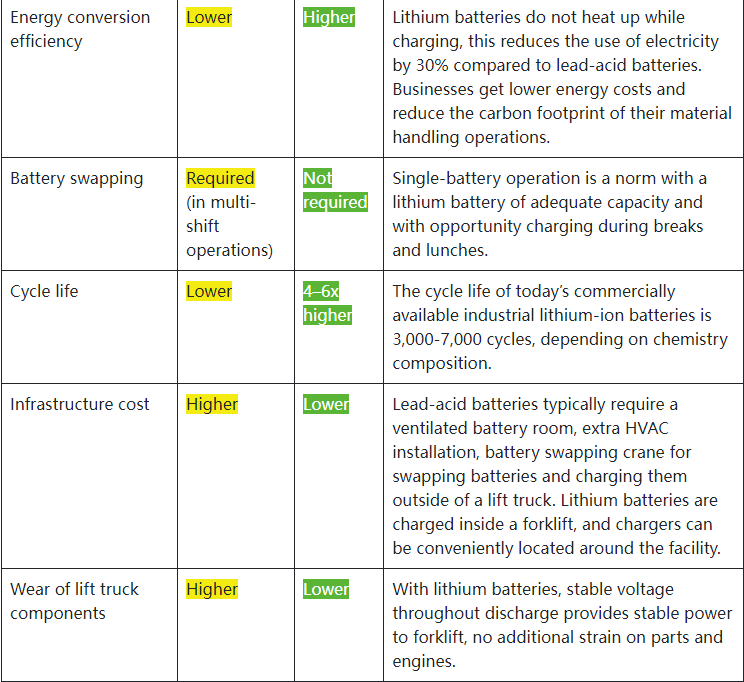
1. Definition and Structure
Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) Batteries
Definition: AGM battery is a sealed lead-acid battery that uses a fiberglass gasket inside to absorb and retain the electrolyte.
Structure: AGM batteries are specially designed and constructed so that the electrolyte is fixed in the fiberglass gasket and does not flow freely. This structure enables the battery to have better sealing and higher energy density.
Lithium-ion battery
Definition: Lithium-ion battery is a rechargeable battery with lithium ions as the main carrier.
Structure: Lithium-ion batteries consist of a positive electrode, a negative electrode, an electrolyte and a separator. The positive electrode material is usually a lithium compound, the negative electrode material is graphite or other carbon materials, and the electrolyte is a lithium salt solution.
2. Working Principle
AGM Battery
The working principle of AGM batteries is similar to that of traditional lead-acid batteries, both of which generate electricity through chemical reactions. However, AGM batteries use glass fiber gaskets to absorb the electrolyte, making the chemical reaction inside the battery more stable, thereby improving the performance and life of the battery.
Lithium-ion battery
The working principle of lithium-ion batteries is the back-and-forth insertion and deintercalation of lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes. During charging, lithium ions are deintercalated from the positive electrode and intercalated into the negative electrode; during discharging, lithium ions are deintercalated from the negative electrode and intercalated into the positive electrode. The energy generated in this process is the output of the battery.
3. Performance characteristics
AGM Battery
High energy density: Because the electrolyte is effectively fixed in the glass fiber mat, AGM batteries have a higher energy density.
Long life: The glass fiber gasket of AGM battery can prevent the free flow of electrolyte, reduce the evaporation and leakage of electrolyte, and thus extend the service life of the battery.
Low self-discharge rate: The glass fiber gasket of AGM battery can prevent the free flow of electrolyte and reduce the rate of self-discharge.
Anti-vibration and anti-leakage: AGM batteries have better anti-vibration and anti-leakage performance, suitable for various application scenarios.
Lithium-ion battery
High energy density: Lithium-ion batteries have high energy density, which gives the battery a higher capacity and longer usage time.
Long life: Lithium-ion batteries have a long cycle life and can withstand many charge and discharge cycles without losing much capacity.
Lightweight: Lithium-ion batteries are relatively lightweight, which makes them widely used in portable devices.
Environmental protection: Lithium-ion batteries do not contain harmful substances such as heavy metals and are environmentally friendly.
4. Application fields
AGM Battery
AGM batteries are widely used in automobiles, motorcycles, UPS systems, solar energy storage systems and other fields. Especially in the automotive field, AGM batteries, as a reliable starting, lighting and ignition (SLI) battery, are widely used in the power systems of traditional fuel vehicles and new energy vehicles.
Lithium-ion battery
Lithium-ion batteries are the mainstream batteries in digital devices, electric vehicles and other fields. With the continuous emergence of new materials and new technologies, the performance of lithium-ion batteries is also constantly improving, and they are expected to be used in more fields in the future.
In summary, there are significant differences between absorbed glass mat (AGM) batteries and lithium-ion batteries in terms of definition, structure, working principle, performance characteristics and application areas. The choice of battery technology depends on the specific application requirements and conditions.




